In MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching), RT (Route Target) and RD (Route Distinguisher) are key components used in Virtual Private Network (VPN) configurations, specifically in MPLS Layer 3 VPNs. They serve different purposes.
Route Distinguisher (RD)
The Route Distinguisher (RD) is a key element in MPLS Layer 3 VPNs that ensures the uniqueness of routes within the network. Its primary function is to allow different VPNs to use the same IP address space without conflict.
- Purpose: Uniquely identifies routes in a VPN.
- Function: Ensures that IP prefixes in different VPNs remain unique, even if they overlap.
- Usage: RD is prepended to the IPv4 address to create a unique VPNv4 address (or VPNv6 for IPv6).
- Scope: RD is locally significant to the MPLS network and used for route uniqueness within the provider's network.
For example, IPv4 routes 10.1.1.0/24 and 10.2.2.0/24 in VPN1 (Customer A) and VPN2 (Customer B) can coexist by using different RDs:
Customer A RD is 100:1
Customer B RD is 200:1
All IP addresses from Customer A once they enter MPLS Service Provider network will become IP prefixes which are unique in MPLS network, thanks to RD value which is unique per customer, like:
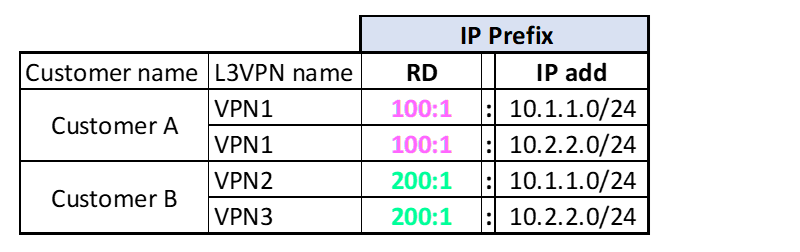
These are now unique IP prefixes, not any more IP addresses, and in that format will be propagated and recognized in MPLS network.
Are RDs Propagated Within the MPLS Network?
Yes, RDs are propagated within the MPLS network, but only as part of VPNv4 or VPNv6 addresses that are advertised between PE routers via MP-BGP.
When a PE router advertises a route from a VRF, it adds the RD to create a unique VPNv4 address. This address is propagated to other PE routers, of course how prefixes are propagated depends on what kind of MPLS architecture you have, full-mesh PEs, or hub and spoke with Route Reflectors or MPLS architecture with Confederations.
RDs are Not Relevant in the Data Plane?
In the data plane, MPLS uses label switching for forwarding traffic, and RD is not part of this process. RD is only a control plane mechanism for distinguishing routes in BGP.
Why RDs are Propagated in the MPLS Network?
RD are propagated because it is essential for the unique identification of routes in the control plane. Here’s why:
o Without RD, IP addresses from different VPNs could conflict. By adding RD, each route becomes unique within the MPLS network.
o Supporting Multi-Tenancy (Multiple Customers). RD allows operators to support multiple customers with overlapping IP address spaces within the same network.
Route Target (RT)
- Purpose: Controls route import/export policies between VPNs.
- Function: Defines which VPN routes are imported into or exported from a VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding instance).
- Usage: RTs are BGP extended communities associated with VPN routes. They dictate:
o Export RT: Marks routes exported from a VRF.
o Import RT: Determines which routes are imported into a VRF.
- Scope: RTs are used across the MPLS network to control route distribution.
For an Example:
Customer A, VRF1 has an Export RT of 100:1 and an Import RT of 200:1.
Customer B, VRF2 has an Export RT of 200:1 and an Import RT of 100:1.
Customer C, VRF3 has an Export RT of 300:1 and an Import RT of 300:1.
This kind of configuration enables route sharing between Customer A and Customer B, and Customer C have completely isolated networks.
Are RTs propagated through the MPLS network?
Yes, RTs are propagated through the MPLS network, but in a specific way. Here's how:
RT is part of BGP attributes?
RT is added as a BGP Extended Community attribute when a route is sent from one VRF. When a PE (Provider Edge) router propagates a route via BGP, the RT is sent along with that route.
RT is not part of MPLS label switching?
Inside the MPLS network (when packets are forwarded between P and PE routers), RT is not relevant for forwarding. MPLS uses only label switching to forward traffic.
RT is used solely in the control plane, i.e., during route exchange via BGP.
Why RTs are propagated?
RT allows PE routers to determine which routes should be imported into which VRFs. When a PE router receives a BGP update with a route and its associated RT, it checks the Import RT configuration in its VRFs:
o If there’s a match, the route is imported into the VRF.
o If there’s no match, the route is ignored.
By separating the control plane (where RT operates) from the data plane (where MPLS labels are used for forwarding), MPLS networks achieve both scalability and flexibility.
To Conclude, is RT Responsible for Placing a Route in the Correct VRF, or RD?
Route Target (RT) is responsible for placing a route in the correct VRF (Virtual Routing and Forwarding) instance, while Route Distinguisher (RD) has a function for route once placed in to correct VRF to keep it unique.


